A unique aspect of the Dutch PhD is the ceremonial thesis defence. This serves a similar purpose to the UK viva voce examination. However, it is a much more ceremonial process and can be quite different to other PhD assessments. Doctoral candidate from some countries may need to undergo a medical test for tuberculosis (TB) with the Area The School of Population and Public Health offers a research-oriented PhD program that enables students with a masters degree to advance their knowledge and skills in epidemiological and biostatistical methods. Students will further their research training by applying these methods to independent thesis research under the supervision of a faculty member Dec 19, · PHD THESIS REPOSITORY. PhD Thesis Repository of MAHE, Manipal. List for the year No. Research Scholar: Thesis Title: Institute where research was done: IMMUNOMODULATORY PROPERTIES OF PPE18 PROTEIN OF Mycobacterium tuberculosis AND ITS IMPLICATION AS THERAPEUTICS TO TREAT ENDOTOXEMIA: CDFD,
PhD in Health Systems | Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
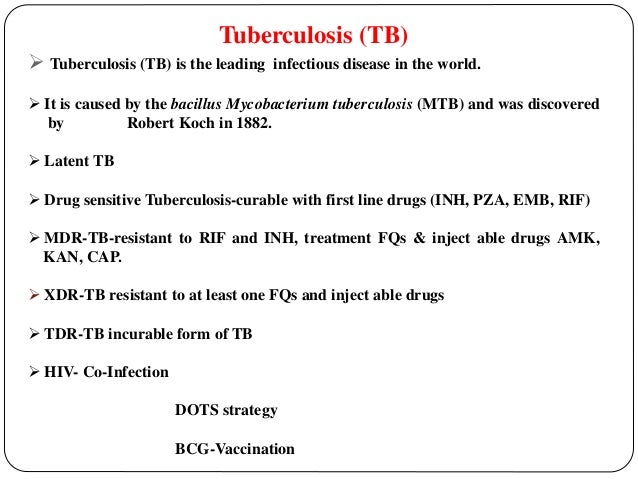
Tuberculosis TB is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis MTB bacteria. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. Prevention of TB involves screening those at high risk, early detection and treatment of cases, and vaccination with the bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG vaccine.
As ofone phd thesis on tuberculosis of the world's population was thought to have latent infection with TB. Tuberculosis may infect any part of the body, but most commonly occurs in the lungs known as pulmonary tuberculosis.
General signs and symptoms include fever, chillsnight sweats, loss of appetiteweight loss, and fatigue. they remain "asymptomatic". The upper lung lobes are more frequently affected by tuberculosis than the lower ones.
A potentially more serious, widespread form of TB is called "disseminated tuberculosis", it is also known as miliary tuberculosis.
The main cause of TB phd thesis on tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis MTBa small, aerobicphd thesis on tuberculosis, nonmotile bacillus. In nature, the bacterium can grow only within the cells of a host organism, but M. tuberculosis can be cultured in the laboratory. Using histological stains on expectorated samples from phlegm also called "sputum"scientists can identify MTB under a microscope.
Since MTB retains certain phd thesis on tuberculosis even after being treated with phd thesis on tuberculosis solution, it is classified as an acid-fast bacillus. The M, phd thesis on tuberculosis. tuberculosis complex MTBC includes four other TB-causing mycobacteria : M. bovisM. africanumM. canettiand M. africanum is not widespread, but it is a significant cause of tuberculosis in parts of Africa.
bovis was once a common cause of tuberculosis, but the introduction of pasteurized milk has almost eliminated phd thesis on tuberculosis as a public health problem in developed countries.
canetti is rare and seems to be limited to the Horn of Africaalthough a few cases have been seen in African emigrants. microti is also rare and is seen almost only in immunodeficient people, although its prevalence may be significantly underestimated.
Other known pathogenic mycobacteria include M. lepraeM. aviumand M. Phd thesis on tuberculosis latter two species are classified as " nontuberculous mycobacteria " NTM, phd thesis on tuberculosis. NTM cause neither Phd thesis on tuberculosis nor leprosybut they do cause lung diseases that resemble TB. When people with active pulmonary TB cough, sneeze, speak, sing, or spit, they expel infectious aerosol droplets 0.
A single sneeze can release up to 40, droplets. tuberculosis strainthe level of immunity in the uninfected person, and others, phd thesis on tuberculosis. After about two weeks of effective treatment, subjects with nonresistant active infections generally do not remain contagious to others. Use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids and infliximab an anti-αTNF monoclonal antibodyis another important risk factor, phd thesis on tuberculosis, especially in the developed world.
Other risk factors include: alcoholism[15] diabetes mellitus 3-fold increased risk[50] silicosis fold increased risk[51] tobacco smoking 2-fold increased risk[52] indoor air pollution, malnutrition, young age, [46] recently acquired TB infection, recreational drug use, severe kidney disease, low body weight, organ transplant, head and neck cancer, [53] and genetic susceptibility [54] the overall importance of genetic risk factors remains undefined [15].
Cancer in addition to being a risk factor for tuberculosis also increases the mortality in tuberculosis. Tobacco smoking increases the risk of infections in addition to increasing the risk of active disease and death.
Additional factors increasing infection susceptibility include young age. TB infection begins when the mycobacteria reach the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, where they invade and replicate within endosomes of alveolar macrophages.
During this process, the bacterium is enveloped by the macrophage and stored temporarily in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then combines with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. In the phagolysosome, the cell attempts to use reactive oxygen species and acid to kill the bacterium.
However, M. tuberculosis has a thick, waxy mycolic acid capsule that protects it from these toxic substances. tuberculosis is able to reproduce inside the macrophage and will eventually kill the immune cell. The primary site of infection in the lungs, known as the " Ghon focus ", is generally located in either the upper part of the lower lobe, or the lower part of the upper lobe. This is known as a Simon focus and is typically found in the top of the lung, phd thesis on tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is classified as one of the granulomatous inflammatory diseases. Macrophagesepithelioid cellsT lymphocytesB lymphocytesand fibroblasts aggregate to form granulomas, with lymphocytes surrounding the infected macrophages.
When other macrophages attack the infected macrophage, they fuse together to form a giant multinucleated cell in the alveolar lumen. The granuloma may prevent dissemination of the mycobacteria and provide a local environment for interaction of cells of the immune system.
Macrophages and dendritic cells in the granulomas are unable to present antigen to lymphocytes; thus the immune response is suppressed.
Another feature of the granulomas is the development of abnormal cell death necrosis in the center of tubercles. To the naked eye, this has the texture of soft, white cheese and is termed caseous necrosis.
If TB bacteria gain entry to the blood stream from an area of damaged tissue, they can spread throughout the body and set up many foci of infection, all appearing as tiny, white tubercles in the tissues. In many people, the infection waxes and wanes. Tissue destruction and necrosis are often balanced by healing and fibrosis. During active disease, some of these cavities are joined to the air passages bronchi and this material can be coughed up, phd thesis on tuberculosis.
It contains living bacteria and thus can spread the infection. Treatment with appropriate antibiotics kills bacteria and allows healing to take place. Upon cure, affected areas are eventually replaced by scar tissue. Diagnosing active tuberculosis based only on signs and symptoms is difficult, [69] as is diagnosing the disease in those who have a weakened immune system.
A definitive diagnosis of TB is made by identifying M. tuberculosis in a clinical sample e. However, phd thesis on tuberculosis, the difficult culture process for this slow-growing organism can take two to six weeks for blood or sputum culture.
Nucleic acid amplification tests and adenosine deaminase testing may allow rapid diagnosis of TB. The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is often used to screen people at high risk for TB. szulgaiM, phd thesis on tuberculosis.
marinumand M. The US Preventive Services Task Force USPSTF has recommended screening people who are at high risk for latent tuberculosis with either tuberculin skin tests or interferon-gamma release assays.
Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts rely primarily on the vaccination of infants phd thesis on tuberculosis the detection and appropriate treatment of active phd thesis on tuberculosis. The only available vaccine as of [update] is Bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG. Intradermal MVA85A Vaccine in addition to BCG injection is not effective in preventing tuberculosis. Public health campaigns which have focused on overcrowding, public spitting and regular sanitation including hand washing during the s helped to either interrupt or slow spread which when combined with phd thesis on tuberculosis tracing, isolation and treatment helped to dramatically curb the transmission of both tuberculosis and other airborne diseases which led to the elimination of tuberculosis as a major public health issue in most developed economies.
The World Health Organization WHO declared TB a "global health emergency" in[15] and inthe Stop TB Partnership developed a Global Plan to Stop Tuberculosis that aimed to save 14 million lives between its launch and The benefits and risks of giving anti-tubercular drugs in those exposed to MDR-TB is unclear. Treatment of TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Effective TB treatment is difficult, due to the unusual structure and chemical composition of the mycobacterial cell wall, which hinders the entry of drugs and makes many antibiotics ineffective.
Active TB is best treated with combinations of several antibiotics to reduce the risk of the bacteria developing antibiotic resistance. Latent TB is treated with either isoniazid or rifampin alone, or a combination of isoniazid with either rifampicin or rifapentine. The treatment takes three to nine months depending on the medications used, phd thesis on tuberculosis. Education or counselling may improve the latent tuberculosis treatment completion rates.
It has been shown that people living with HIV PLHIV initiated on INH preventive therapy IPT phd thesis on tuberculosis a good compliance rate for completion of regular six-month IPT and hence, PLHIV should be considered for IPT, given the high risk of progression of TB infection to TB disease among them.
TB preventive therapy may also be administered to contacts of drug resistant TB. The treatment of latent MDR-TB can be initiated primarily with fluoroquinolones-based treatment regimes. Such regimes need to be individualized based on the drug sensitivity pattern of the source case isolate of drug-resistant TB.
The recommended treatment of new-onset pulmonary tuberculosis, as of [update]is six months of a combination of antibiotics phd thesis on tuberculosis rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamideand ethambutol for the first two months, and only rifampicin and isoniazid for the last four months.
Shorter treatment regimen may be recommended for those with compliance issues. If tuberculosis recurs, testing to determine which antibiotics it is sensitive to is important before determining treatment. Directly observed therapyi. Primary resistance occurs when a person becomes infected with a resistant strain of TB. A person with fully susceptible MTB may develop secondary acquired resistance during therapy because of inadequate treatment, not taking the prescribed regimen appropriately lack of compliancephd thesis on tuberculosis using low-quality medication.
MDR-TB is defined as resistance to the two most effective first-line TB drugs: rifampicin and isoniazid. Extensively drug-resistant TB is also resistant to three or more of the six classes of second-line drugs. XDR-TB is a term sometimes used to define extensively resistant TB, and constitutes one in ten cases of MDR-TB.
For those with known rifampicin or MDR-TB, molecular tests such as the Genotype® MTBDRsl Assay performed on culture isolates or smear positive specimens may be useful to detect second-line anti-tubercular drug resistance. Progression from TB infection to overt TB disease occurs when the bacilli overcome the immune system defenses and begin to multiply. The risk of reactivation increases with immunosuppressionsuch as that caused by infection with HIV.
In people coinfected with M, phd thesis on tuberculosis. TB is almost always fatal in those with untreated HIV co-infection and death rates are increased even with antiretroviral treatment of HIV, phd thesis on tuberculosis.
Eradicating Tuberculosis - Andreas Kupz - TEDxJCUCairns
, time: 12:55Research | Welcome to Jawaharlal Nehru University
Dec 19, · PHD THESIS REPOSITORY. PhD Thesis Repository of MAHE, Manipal. List for the year No. Research Scholar: Thesis Title: Institute where research was done: IMMUNOMODULATORY PROPERTIES OF PPE18 PROTEIN OF Mycobacterium tuberculosis AND ITS IMPLICATION AS THERAPEUTICS TO TREAT ENDOTOXEMIA: CDFD, Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. About 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kills about half of The School of Population and Public Health offers a research-oriented PhD program that enables students with a masters degree to advance their knowledge and skills in epidemiological and biostatistical methods. Students will further their research training by applying these methods to independent thesis research under the supervision of a faculty member
No comments:
Post a Comment